Paula and Bobby
Parents of Lillie
Finger Syndactyly
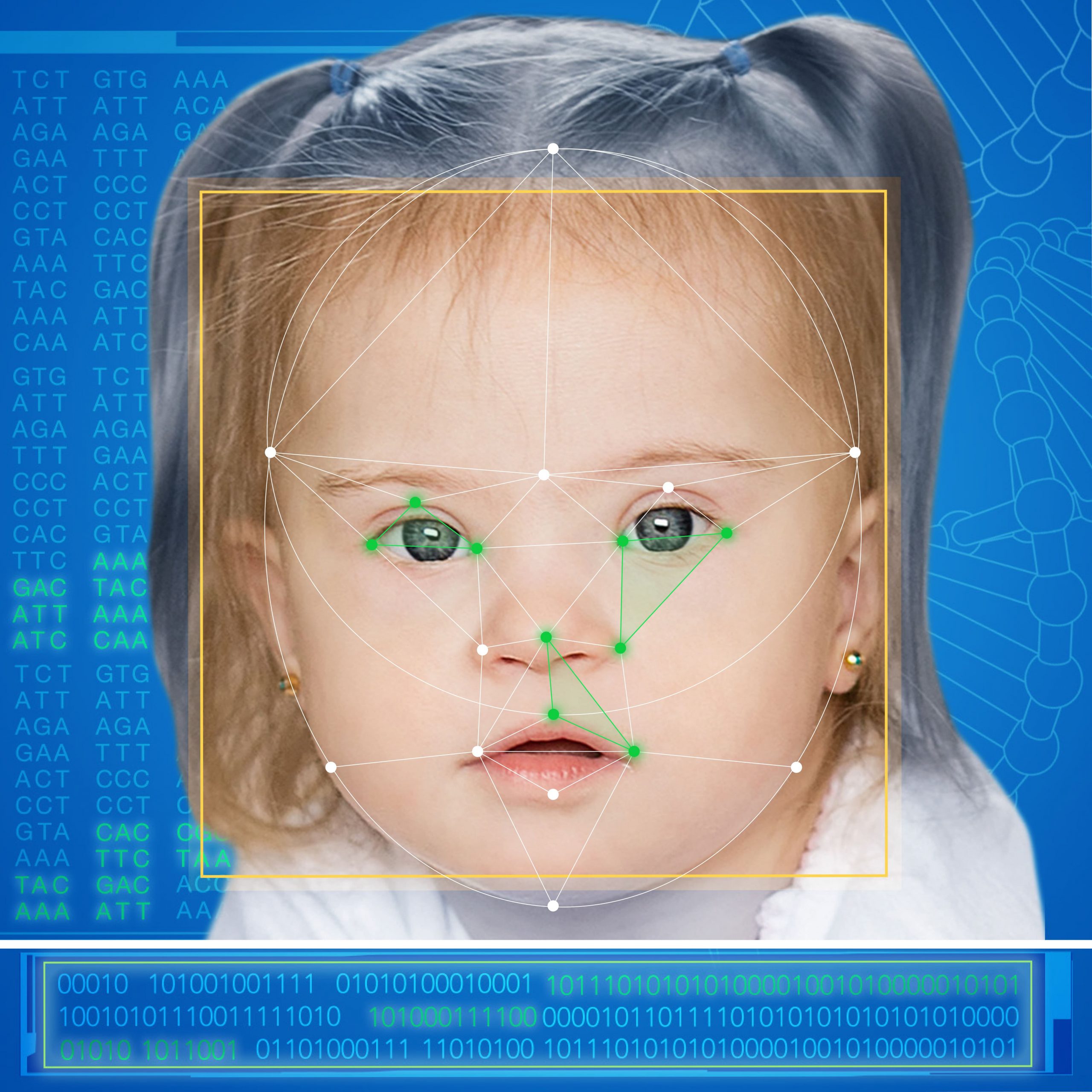
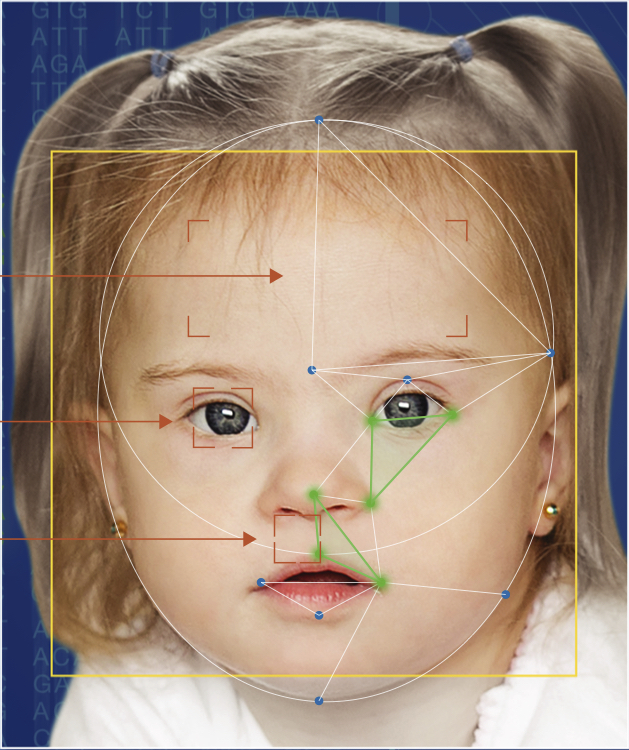
Understanding limb related symptoms and features.
Symptoms may affect multiple parts of the body. Understanding which part of the body a symptom affects, can help us to better understand the potential underlying causes of a symptom, including a rare disease or genetic syndrome.
Limbs refer to the arms and legs of the body. They also include the hands and feet connected to the main limbs. Parts of the limbs include the fingers and toes, known as digits.
The limbs are an essential part of many different functions of the body, including movement, feeding and other necessary daily skills. Symptoms and features affecting the development and functioning of the limbs may also impact on these activities as well.
Generally, symptoms affecting the limbs may be seen with the naked eye. Although diagnosing a limb related symptom may involve different tests and assessments, both subjective and objective.
What is finger syndactyly?
Finger syndactyly is a webbing or fusion of fingers, connecting two fingers to each other in an abnormal way. Any two fingers or more may be partially or completely involved.
When the connection includes bone fusion, it is referred to in some cases as bony or complex syndactyly, or as symphalangism in others.
Syndactyly can be corrected surgically.
Fused or conjoined fingers may be congenital, or some cases may result from environmental exposure of the fetus during gestation, or both, or the causes may remain unknown.
Finger syndactyly can also manifest as part of underlying genetic diseases or syndromes. However, this diagnosis also depends on other accompanying features.
Most cases of failure to thrive have a combination of organic and nonorganic causes.
Organic FTT may be detected at any age, depending on the disorder that is causing it. Nonorganic FTT will usually be noticeable before the child is one year old, and often by 6 months.
Medical problems that can cause failure to thrive can be minor and relatively easy to correct. For example, a cleft lip or cleft palate could cause trouble chewing or swallowing. Some other disorders may also stop the child from absorbing, retaining, or processing the food that they do eat. Infections, tumors, diseases, syndromes or metabolic disorders could also cause FTT. It is rare for FTT to result from inadequate breast milk production or low fat content.
What should I do next?
In some instances, finger syndactyly may be one of the features of a rare disease or genetic syndrome. In this case fast, targeted genetic analysis can give you a more accurate diagnosis.
Synonyms:
Partial syndactyly, conjoined fingers, webbed fingers, fused fingers, complex syndactyly, bony syndactyly, symphalangism
HPO:
0006101
Optional syndromes:
Clarify any concerns you may have and get tested online today!
Schedule Your Online Meeting Now
Synonyms:
Partial syndactyly, conjoined fingers, webbed fingers, fused fingers, complex syndactyly, bony syndactyly, symphalangism
HPO:
-
0006101
Optional syndromes:
FDNA™ Health can help you with the diagnostic journey.
Learn about child developmental delays: Causes, Symptoms, and Therapies.
Don't wait years for a diagnosis. Act now and save valuable time.
Explore the most detected symptoms in our system (numbers are global and based on the data from 120 countries):
What is FDNA Health?
With the largest global database and a leading decision-support tool using AI, FDNA™ Health enables patients and their families to better understand symptoms and conditions with the goal of shortening the time to diagnosis.
Benefits of FDNA Health
Save valuable time by
learning about possible conditions
and report to your clinician
Advanced AI technology
and leading worldwide clinicians
shortening time to diagnosis
Looking for answers?
Worried about child development?
We are here to help you!